AIPL RESEARCH REPORT
SCC9
(3-08) |
Somatic cell counts of milk from Dairy Herd
Improvement herds during 2007R.H. Miller, H.D. Norman, and L.L.M.
Thornton
Animal Improvement Programs Laboratory, ARS-USDA, Beltsville, MD
20705-2350
301-504-8334 (voice) ~ 301-504-8092 (fax) ~
rlaipl@aipl.arsusda.gov ~
http://aipl.arsusda.gov |
Test-day data from all herds enrolled in Dairy Herd Improvement
(DHI) somatic cell testing during 2007 (94% of all DHI
herds) were examined to assess the status of national milk quality. All
test-day data within a herd were included regardless of breed; data from
owner-sampler herds were included as well. Data from cows with records that
failed some Animal Improvement Programs Laboratory (AIPL) editing
procedures were excluded. Somatic cell score (SCS) is reported to AIPL
as part of an individual cow's test-day yield information. It was converted
back to SCC in cells/milliliter [SCC = 2(SCS–3) × 100,000] for calculating herd and
State averages.
Table 1 shows the total number of herd test days, the
average number of cows (with usable records) per herd on test day, the average
test-day milk yield and SCC, and the percentages of herd test days that
exceeded four levels of SCC (750,000, 600,000, 500,000, and 400,000 cells/ml)
for each State during 2007. The current
legal limit for bulk
tank SCC is 750,000 cells/ml for Grade A producers; the lower limits shown
have been proposed on a number of occasions as future maximums by the National
Mastitis Council. An interesting development is that California lowered their
state standard for legal milk to 600,000 cells/ml. State and national average
daily milk yields were weighted by the number of cows per herd test day. Herd,
State, and national average SCC's were based on SCC's from individual cows that
were weighted by milk yield on test day. Percentages of herd test days by level
of SCC are for herd test days that included records of at least ten cows.
Nationally, average SCC during 2007 was 276,000 cells/ml, which is considerably
lower (by 12,000 cells/ml) than last year. A majority of states (27) had lower
average SCC than last year; 21 states had higher.
Variation among States (Table 1) was large. State
average SCC's were often lower than the national average in the Northeast,
upper Midwest, and the far West and higher in the Southeast, Mid-Atlantic, and
Central states, a finding consistent with previous reports. Although climatic
conditions (temperature and humidity) surely contributed to regional SCC
differences, differences between adjacent states were substantial, suggesting
mastitis-control practices are impacting State differences as well.
Corresponding averages for earlier years 1995 through 2007 are in
Table 2. This is the third year in a row that SCC has
declined. It has improved for five of the last six years, declining from a high
of 322,000 cells/ml in 2001. The percentage of herd test days that exceeded
750,000, 600,000, 500,000, and 400,000 cells/ml during 2007 was 3.5, 7.6, 13.4,
and 24.0, respectively. The overall percentage of herd test days exceeding all
levels were lower than in 2006. In 2007, 3.5% of test days from DHI herds that
participated in somatic cell testing were higher than the present legal limit
for SCC of bulk tank milk. This percentage may overestimate the percentage of
herds that shipped milk exceeding the legal limit for bulk tank SCC on test day
because the milk of cows treated for mastitis is excluded from the bulk tank
even though included in DHI test data. Also, the percentage of herd test days
that exceeded the legal limit would have been higher than the percentage of
herds that were rejected from the market because market exclusion only occurs
after repeat violations.
Herd size and average daily milk yield have been increasing over the
period reported (Table 2). The large increase in cows per
herd for 2005 to 2006 (90.3 vs. 115.5 was due in part to a change in policy of
accepting records missing sire identification into the national database. The
increase in cows per herd between 2006 and 2007 was substantial (115.5 vs.
125.1). The decline in SCC over the last six years is encouraging; hopefully
average SCC will continue to decline in the future due to both improved
management practices and genetic selection. The trends for lower percentage of
herd test days above three thresholds (600,000, 500,000 and 400,000 cells/ml)
is likewise encouraging. The concerted effort to improve milk quality needs to
continue. State and national SCC's in DHI will continue to be summarized
annually so changes in SCC and implications to milk quality can be monitored.
Table 3 provides milk yield and SCC by estimated herd
size. As herd size increased, average daily milk generally increased, and
average SCC declined until herd size exceeded 3000 cows. The most disturbing
result is the percentage of test days with over 750,000 cells/ml. For herds
with less than 50 cows, this occurred 5.9% of the time. It occurred on only
2.0% and only 1.3% of the test days for herds with 50 to 99 and 100 to 149
cows, respectively, and averaged 0.7% of the test days for the remaining large
herds.
Table 4 provides the same statistics for all herds by
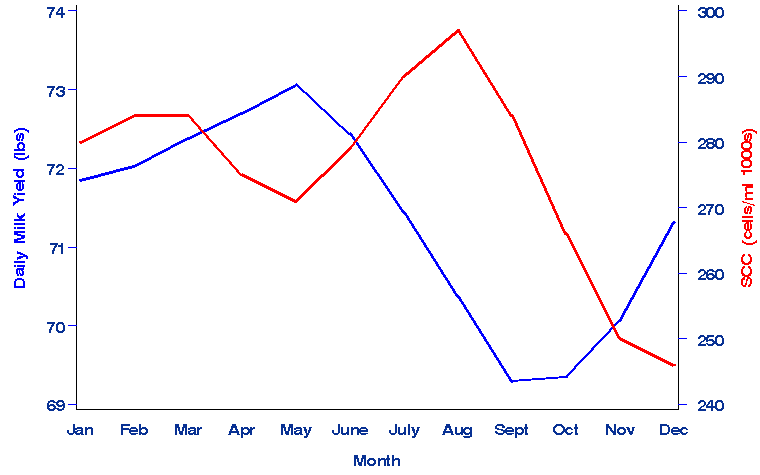
month. The seasonal pattern of milk quality is illustrated in Figure 1. Milk yield per cow was highest in the late winter and
spring. Milk yield declined during the summer months. SCC increased from May
through August, then decreased from September through December. The highest
quality milk was produced in October, November, and December.
Table 1. Characteristics of DHI herd test days
for milk yield and SCC of milk by State during 2007.
SCC characteristics
| |
Herd test days1 |
Cows2 per herd |
Average daily milk yield |
Average SCC |
Herd test days3 with SCC greater than |
| State |
(no.) |
(no.) |
(lbs) |
(cells/ml, 1000's) |
750,000 cells/ml
(%) |
600,000 cells/ml
(%) |
500,000 cells/ml
(%) |
400,000 cells/ml
(%) |
| Alabama |
238 |
122.3 |
50.6 |
407 |
4.2 |
10.1 |
22.7 |
42.9 |
| Arizona |
264 |
1451.6 |
69.6 |
257 |
0.0 |
0.8 |
1.9 |
7.6 |
| Arkansas |
329 |
108.4 |
55.1 |
441 |
15.8 |
24.9 |
35.6 |
53.5 |
| California |
9,327 |
702.0 |
73.9 |
253 |
2.4 |
4.8 |
7.7 |
13.7 |
| Colorado |
343 |
689.0 |
69.3 |
268 |
1.2 |
3.5 |
7.9 |
14.3 |
| Connecticut |
807 |
92.6 |
67.5 |
285 |
3.6 |
6.7 |
11.5 |
20.0 |
| Delaware |
251 |
116.2 |
68.3 |
320 |
2.4 |
4.4 |
8.8 |
20.3 |
| Florida |
222 |
755.6 |
69.0 |
333 |
8.6 |
18.5 |
27.0 |
50.9 |
| Georgia |
1,134 |
134.7 |
61.2 |
422 |
6.7 |
17.8 |
31.7 |
51.8 |
| Idaho |
1,718 |
684.9 |
75.5 |
255 |
1.7 |
3.8 |
8.1 |
14.7 |
| Illinois |
4,427 |
86.0 |
69.5 |
294 |
3.0 |
7.4 |
13.9 |
26.7 |
| Indiana |
3,621 |
84.8 |
69.1 |
306 |
4.6 |
9.6 |
15.6 |
28.6 |
| Iowa |
8,918 |
91.9 |
71.0 |
304 |
4.2 |
9.6 |
16.3 |
29.3 |
| Kansas |
2,021 |
95.7 |
66.6 |
360 |
6.8 |
14.4 |
22.8 |
37.9 |
| Kentucky |
1,721 |
79.8 |
63.3 |
354 |
6.0 |
14.3 |
23.8 |
39.7 |
| Louisiana |
448 |
106.2 |
51.2 |
446 |
13.6 |
29.0 |
42.4 |
60.7 |
| Maine |
1,208 |
72.3 |
63.7 |
267 |
3.1 |
6.5 |
12.7 |
21.5 |
| Maryland |
3,616 |
80.3 |
66.3 |
284 |
3.3 |
7.4 |
12.3 |
22.2 |
| Massachusetts |
831 |
79.2 |
68.2 |
276 |
2.0 |
5.2 |
9.7 |
17.9 |
| Michigan |
7,678 |
151.4 |
78.1 |
247 |
2.3 |
4.8 |
8.6 |
16.5 |
| Minnesota |
25,131 |
78.6 |
69.9 |
320 |
4.7 |
10.3 |
18.1 |
31.3 |
| Mississippi |
336 |
162.6 |
64.9 |
337 |
2.4 |
10.4 |
18.2 |
41.1 |
| Missouri |
3,399 |
65.5 |
58.3 |
356 |
6.9 |
13.7 |
21.8 |
36.5 |
| Montana |
400 |
115.9 |
75.2 |
200 |
0.0 |
0.5 |
2.0 |
6.3 |
| Nebraska |
1,591 |
127.0 |
68.1 |
331 |
6.2 |
12.5 |
21.5 |
36.0 |
| Nevada |
116 |
540.5 |
78.3 |
306 |
7.8 |
7.8 |
11.2 |
12.9 |
| New Hampshire |
873 |
84.5 |
69.9 |
245 |
1.8 |
4.2 |
8.4 |
17.1 |
| New Jersey |
565 |
63.8 |
65.8 |
344 |
4.4 |
10.3 |
18.6 |
33.3 |
| New Mexico |
255 |
1391.4 |
70.8 |
289 |
5.5 |
7.1 |
12.9 |
19.2 |
| New York |
20,265 |
112.4 |
71.2 |
258 |
2.4 |
5.8 |
11.0 |
20.5 |
| North Carolina |
1,644 |
125.8 |
68.2 |
324 |
2.0 |
6.1 |
12.9 |
26.9 |
| North Dakota |
384 |
88.2 |
69.3 |
320 |
2.1 |
4.2 |
10.7 |
22.4 |
| Ohio |
8,534 |
89.1 |
68.8 |
317 |
3.6 |
8.1 |
14.9 |
26.7 |
| Oklahoma |
582 |
123.6 |
57.9 |
343 |
6.7 |
15.1 |
27.5 |
44.3 |
| Oregon |
2,255 |
154.4 |
67.6 |
228 |
2.8 |
4.6 |
7.6 |
12.0 |
| Pennsylvania |
42,727 |
59.4 |
69.4 |
296 |
3.0 |
7.2 |
13.2 |
24.1 |
| Puerto Rico |
956 |
110.5 |
36.1 |
499 |
18.5 |
30.3 |
45.5 |
63.4 |
| Rhode Island |
41 |
73.0 |
62.6 |
160 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
9.8 |
| South Carolina |
538 |
161.2 |
62.8 |
355 |
2.0 |
5.2 |
12.3 |
33.1 |
| South Dakota |
1,372 |
154.3 |
71.2 |
288 |
5.4 |
12.7 |
22.2 |
36.2 |
| Tennessee |
1,525 |
86.7 |
59.6 |
418 |
5.2 |
14.8 |
27.6 |
49.6 |
| Texas |
1,563 |
396.4 |
61.5 |
318 |
2.8 |
6.5 |
12.5 |
26.2 |
| Utah |
1,397 |
163.8 |
69.0 |
242 |
2.6 |
4.8 |
8.3 |
16.7 |
| Vermont |
3,478 |
101.0 |
67.6 |
230 |
1.5 |
3.5 |
6.7 |
13.6 |
| Virginia |
4,034 |
107.3 |
68.5 |
309 |
2.0 |
5.6 |
10.9 |
23.8 |
| Washington |
1,842 |
240.5 |
74.4 |
237 |
2.0 |
2.9 |
4.6 |
8.7 |
| West Virginia |
409 |
84.8 |
60.1 |
324 |
3.7 |
8.3 |
18.8 |
33.0 |
| Wisconsin |
52,264 |
80.9 |
74.5 |
258 |
3.3 |
6.7 |
11.2 |
19.8 |
| Wyoming |
28 |
162.5 |
70.9 |
320 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
7.1 |
| United States |
227,626 |
125.1 |
71.4 |
276 |
3.5 |
7.6 |
13.4 |
24.0 |
| 1All herd test days with usable records. |
| 2Cows with usable records (less than total cows on test). |
| 3Herd test days with ≥10 usable records. |
Table 2. National averages of herd test days for
milk yield and SCC of milk by year.
SCC characteristics
| |
Herd test days1 |
Cows2 per herd |
Average daily milk yield |
Average SCC |
Herd test days3 with SCC greater than |
| Year |
(no.) |
(no.) |
(lbs) |
(cells/ml, 1000's) |
750,000 cells/ml
(%) |
600,000 cells/ml
(%) |
500,000 cells/ml
(%) |
400,000 cells/ml
(%) |
| 1995 |
265,844 |
50.0 |
65.3 |
304 |
4.1 |
9.3 |
16.0 |
27.2 |
| 1996 |
255,039 |
55.5 |
64.7 |
308 |
4.1 |
9.2 |
16.1 |
27.8 |
| 1997 |
287,789 |
57.4 |
66.4 |
314 |
4.2 |
9.5 |
16.6 |
28.8 |
| 1998 |
283,695 |
60.8 |
66.8 |
318 |
4.5 |
10.1 |
17.8 |
30.3 |
| 1999 |
273,364 |
67.0 |
68.2 |
311 |
4.3 |
9.7 |
17.1 |
29.8 |
| 2000 |
260,139 |
73.3 |
69.1 |
316 |
4.1 |
9.4 |
16.8 |
29.5 |
| 2001 |
244,940 |
79.1 |
69.0 |
322 |
4.9 |
10.6 |
18.2 |
31.1 |
| 20024 |
267,809 |
77.5 |
69.5 |
320 |
5.6 |
11.0 |
18.1 |
30.0 |
| 2003 |
251,182 |
80.5 |
69.6 |
319 |
5.6 |
11.2 |
18.4 |
30.4 |
| 2004 |
240,938 |
85.7 |
69.4 |
295 |
4.7 |
9.4 |
15.5 |
26.4 |
| 2005 |
234,585 |
90.3 |
71.1 |
296 |
4.7 |
9.2 |
15.3 |
25.8 |
| 20065 |
236,191 |
115.5 |
71.2 |
288 |
3.9 |
8.3 |
14.3 |
25.2 |
| 2007 |
227,626 |
125.1 |
71.4 |
276 |
3.5 |
7.6 |
13.4 |
24.0 |
| Annual trend |
-3,853 |
5.4*** |
0.5*** |
-2.1* |
0.0 |
-0.1 |
-0.2 |
-0.3 |
| 1All herd test days with usable records. |
| 2Cows with usable records (less than total cows on test). |
| 3Herd test days with ≥10 usable records. |
| 4Summary characteristics for 2002 were recalculated to include more complete data than was available at the time of initial reporting. |
| 5Cows per herd included those records missing sire identification starting in 2006; they were not included in prior years. |
*The linear regression was significant with P ≤ .05
**The linear regression was significant with P ≤ .01
***The linear regression was significant with P ≤ .001 |
Table 3. Characteristics of DHI herd test days
for milk yield and SCC during 2007 by herd size.
SCC characteristics by herd size
| Herd size1 |
Herd test days2 |
Cows3 per herd |
Average daily milk yield |
Average SCC |
Herd test days4 with SCC greater than |
| (cows) |
(no.) |
(no.) |
(lbs) |
(cells/ml, 1000's) |
750,000 cells/ml
(%) |
600,000 cells/ml
(%) |
500,000 cells/ml
(%) |
400,000 cells/ml
(%) |
| <50 |
102,909 |
29.1 |
62.5 |
316 |
5.9 |
11.3 |
17.9 |
28.5 |
| 50 - 99 |
69,230 |
69.1 |
66.9 |
300 |
2.0 |
5.9 |
12.0 |
23.8 |
| 100 - 149 |
20,132 |
120.4 |
67.8 |
284 |
1.3 |
4.0 |
8.7 |
19.2 |
| 150 - 199 |
9,273 |
172.3 |
70.0 |
277 |
0.7 |
3.1 |
7.1 |
17.4 |
| 200 - 299 |
8,642 |
242.8 |
71.4 |
273 |
0.6 |
2.3 |
6.3 |
15.9 |
| 300 - 499 |
7,495 |
385.4 |
74.1 |
267 |
0.7 |
2.0 |
4.6 |
12.1 |
| 500 - 999 |
5,763 |
688.8 |
75.8 |
266 |
1.0 |
2.7 |
5.3 |
12.5 |
| 1000 - 1999 |
3,004 |
1364.3 |
76.0 |
261 |
0.5 |
1.3 |
3.3 |
9.5 |
| 2000 - 2999 |
741 |
2441.3 |
75.1 |
243 |
0.5 |
0.9 |
1.9 |
6.3 |
| >3000 |
437 |
4136.8 |
75.3 |
253 |
0.0 |
0.5 |
2.5 |
5.7 |
| All herds |
227,626 |
125.1 |
71.4 |
276 |
3.5 |
7.6 |
13.4 |
24.0 |
| 1Number of cows reported in milk. |
| 2All herd test days with usable records. |
| 3Cows with usable records (less than total cows on test). |
| 4Herd test days with ≥10 usable records. |
Table 4. Characteristics of DHI herd test days
for milk yield and SCC during 2007 by month.
SCC seasonal characteristics
| |
Herd test days1 |
Cows2 per herd |
Average daily milk yield |
Average SCC |
Herd test days3 with SCC greater than |
| Month |
(no.) |
(no.) |
(lbs) |
(cells/ml, 1000's) |
750,000 cells/ml
(%) |
600,000 cells/ml
(%) |
500,000 cells/ml
(%) |
400,000 cells/ml
(%) |
| January |
19,092 |
121.1 |
71.8 |
280 |
3.4 |
7.3 |
12.5 |
22.4 |
| February |
18,030 |
124.1 |
72.0 |
284 |
3.7 |
7.5 |
13.0 |
22.9 |
| March |
20,499 |
125.4 |
72.4 |
284 |
3.6 |
7.8 |
13.5 |
23.9 |
| April |
18,726 |
125.6 |
72.7 |
275 |
3.4 |
7.2 |
12.7 |
22.6 |
| May |
19,398 |
124.6 |
73.1 |
271 |
3.0 |
6.4 |
11.5 |
21.6 |
| June |
19,227 |
124.4 |
72.4 |
279 |
3.4 |
7.5 |
13.2 |
23.9 |
| July |
18,630 |
123.7 |
71.4 |
290 |
4.3 |
9.4 |
16.3 |
28.3 |
| August |
18,813 |
126.9 |
70.4 |
297 |
4.9 |
10.6 |
18.5 |
31.1 |
| September |
18,759 |
125.6 |
69.3 |
284 |
3.8 |
8.7 |
15.2 |
27.2 |
| October |
18,908 |
126.3 |
69.4 |
266 |
3.3 |
7.7 |
13.6 |
24.4 |
| November |
18,820 |
126.2 |
70.1 |
250 |
2.5 |
5.7 |
10.5 |
19.8 |
| December |
18,724 |
127.0 |
71.3 |
246 |
2.5 |
5.8 |
10.4 |
19.8 |
| Yearly |
227,626 |
125.1 |
71.4 |
276 |
3.5 |
7.6 |
13.4 |
24.0 |
| 1All herd test days with usable records. |
| 2Cows with usable records (less than total cows on test). |
| 3Herd test days with ≥10 usable records. |
Figure 1. Average daily milk yield and SCC during 2007 by month.
SCC seasonal characteristics